Whitefly Integrated Control
Why Effective Whitefly Control Matters
If you’re managing large-scale vegetable fields, greenhouses, orchards, or ornamental nurseries, whiteflies are one of the most persistent and economically damaging pests you face. These tiny sap-sucking insects are not only capable of rapid population explosions in warm climates, but they also cause extensive plant damage, spread viruses, and contaminate leaves and fruit with honeydew and black sooty mold.
Once established, whitefly infestations are difficult to reverse without fast-acting and properly selected insecticides. Relying solely on environmental factors or natural predators may not deliver consistent or sufficient results—especially under commercial production timelines where yield loss translates directly into revenue loss.
At POMAIS, we support agricultural input distributors and growers with professional-grade insecticide solutions that are designed to:
- Deliver quick knockdown of whitefly adults and nymphs
- Penetrate leaf surfaces to control hidden or resistant stages
- Maintain control over multiple generations with long-lasting action
- Fit seamlessly into high-frequency production cycles with minimal phytotoxicity
This guide will help you understand:
- How to identify key whitefly species
- The damage they cause across crop types
- The most effective insecticide categories and active ingredients
- How POMAIS products can support your control program through custom formulations and flexible supply
If whiteflies are compromising your crop quality or creating product rejection risks, now is the time to implement a chemical control plan that works. Let’s begin with how to correctly identify the pest before treatment.
Key Identification Features of Whiteflies
Accurate identification is essential before selecting any control strategy. Whiteflies may be small, but their biological traits make them highly adaptable and destructive—especially in warm, irrigated environments where they breed rapidly and target a wide range of crops and ornamentals.
Whiteflies are not true flies (Diptera) but belong to the insect order Hemiptera, closely related to aphids and scales. They are characterized by their soft yellowish bodies and four powdery-white wings. While adults are easy to spot on the underside of leaves, the more damaging stage is often the nymph, particularly the later immature stages which feed heavily and remain immobile.
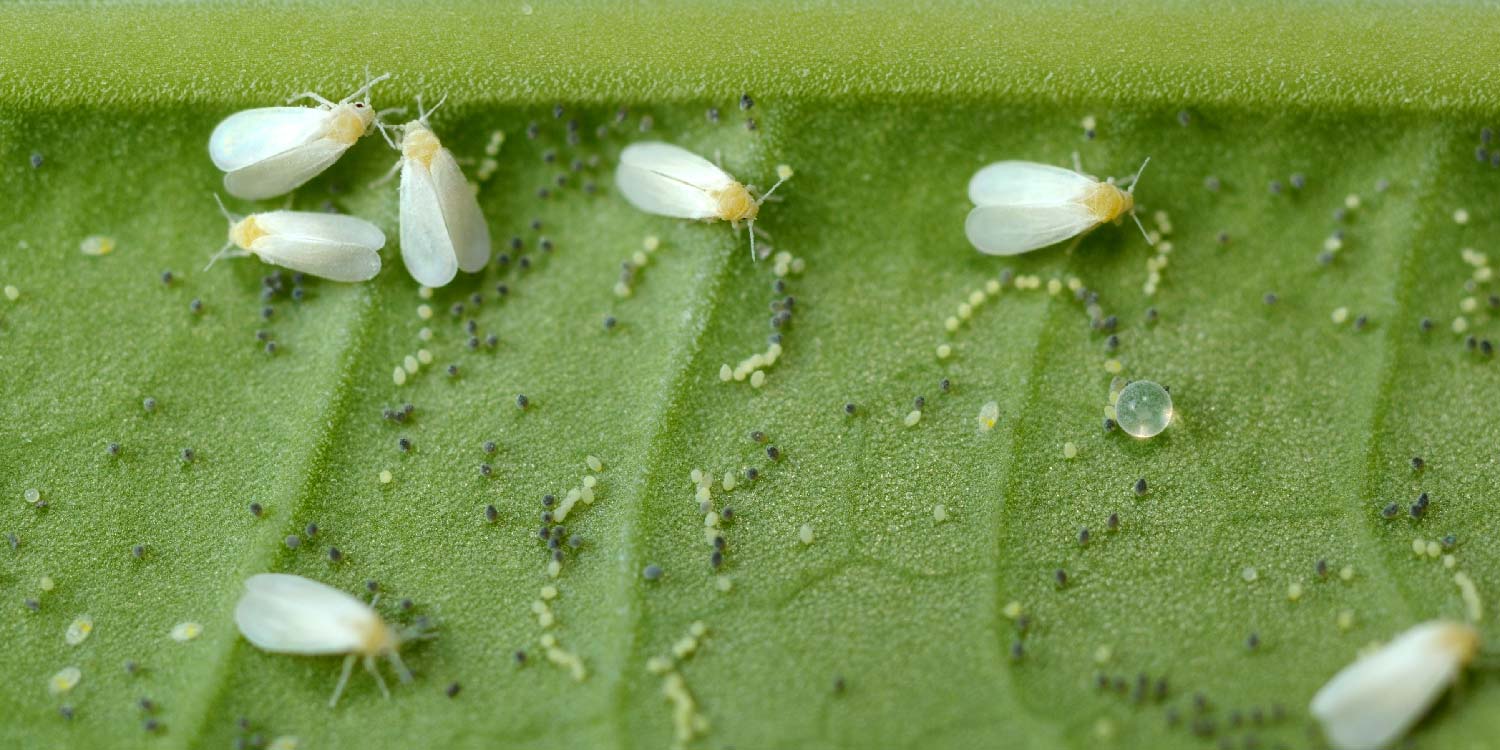

Key Life Stages to Watch
- Eggs: Tiny, oblong, usually deposited in circles or spirals on the underside of leaves.
- First Instar (Crawler): Only mobile immature stage; disperses briefly before settling.
- Later Nymphs (Instars 2–4): Immobile, flat, oval-shaped. Often mistaken for scale insects. This is the most critical stage to target with systemic insecticides.
- Adults: Winged, white, and visible when disturbed. Adults are the reproductive stage, and their elimination is essential to halt egg-laying.
Common Pest Species to Monitor
- Greenhouse Whitefly (Trialeurodes vaporariorum)
Found on vegetables, herbs, and ornamentals. Recognized by long waxy filaments around mature nymphs. - Sweetpotato Whitefly (Bemisia tabaci)
One of the most economically damaging species. Feeds on vegetables, cotton, and many ornamentals. Adults hold their wings at a slight angle and nymphs lack waxy fringes. - Giant Whitefly (Aleurodicus dugesii)
Easily identified by its long wax spirals and large white adults. Common in tropical ornamentals. - Citrus Whitefly, Mulberry Whitefly, and Woolly Whitefly
Found in orchards and landscaping systems. Their nymphs often have distinctive wax patterns, making visual diagnosis possible with basic magnification.
Understanding which species you’re facing—and the proportion of adults versus nymphs—allows you to select the appropriate formulation (contact vs. systemic) and application method (foliar vs. soil treatment). At POMAIS, we help our partners match insecticide recommendations not only by crop but by target species and development stage, ensuring higher control rates and fewer repeat applications.
Whitefly Damage in Field and Greenhouse Systems
Whiteflies are not merely a nuisance—they are a high-impact pest capable of causing significant crop damage, economic losses, and post-harvest quality degradation. If left unchecked, even moderate populations can escalate quickly in warm, humid environments, especially in protected structures like greenhouses or under intensive irrigation systems.
Direct Plant Damage
- Sap Extraction and Leaf Deformation
Nymphs and adults pierce the phloem to suck plant juices, leading to leaf yellowing, curling, desiccation, and premature drop. In crops like tomato, pepper, and cotton, this weakens the plant, reducing yield and fruit quality. - Stunted Growth and Plant Decline
Continuous feeding from multiple generations weakens young plants, delays maturity, and can cause widespread plant collapse in high-pressure situations. - Honeydew Production and Black Sooty Mold
As whiteflies feed, they excrete large volumes of sticky honeydew. This residue encourages the growth of black sooty mold, reducing photosynthetic capacity and contaminating produce. Leaf surfaces become unsightly, reducing the market value of leafy vegetables and ornamental crops.
Virus Transmission and Crop Loss
- Certain whitefly species, especially Bemisia tabaci (sweetpotato whitefly), act as vectors for serious plant viruses, including:
- Tomato yellow leaf curl virus (TYLCV)
- Cucurbit yellow stunting disorder virus
- Cotton leaf curl virus
- Viral diseases spread rapidly through fields and greenhouses, and insecticide-based whitefly control is the only reliable method of breaking the infection cycle.
Commercial and Post-Harvest Impact
- Residue concerns: Honeydew and sooty mold can lead to export rejection in high-value vegetable shipments.
- Visual degradation: Ornamental plant quality declines sharply under whitefly infestation.
- Increased labor: Growers must spend more on pruning, cleaning, and replacing damaged plants.
- Input inefficiencies: Whiteflies reduce the efficiency of irrigation, fertilization, and foliar nutrient uptake by damaging the foliage.
In high-density production systems, whiteflies cannot be managed effectively without targeted chemical control. Contact insecticides may eliminate adults quickly, but only systemic and translaminar products can penetrate the leaf surface and eliminate the feeding nymphs—the stage responsible for most economic damage.
POMAIS offers insecticide solutions specifically designed to:
- Interrupt virus transmission pathways
- Suppress both adult and nymphal stages
- Maintain leaf health and crop vigor under pest pressure
Chemical Control as the Primary Management Strategy
When facing aggressive whitefly infestations—particularly in high-value crops such as tomatoes, cucurbits, peppers, and ornamentals—chemical insecticides remain the most effective and scalable solution. In many commercial operations, environmental and biological controls are insufficient to halt pest outbreaks or prevent virus spread in time. This is where professional-grade insecticides from POMAIS deliver maximum impact.
Why Insecticides Are Essential
- Rapid Knockdown of Adults
Eliminating the reproductive population prevents egg-laying and suppresses immediate expansion. Contact insecticides are ideal for this stage, especially during initial outbreaks. - Systemic Penetration of Immature Stages
Whitefly nymphs (especially 2nd–4th instars) are immobile and located on leaf undersides—only systemic and translaminar insecticides can reach and eliminate them effectively. - Virus Transmission Suppression
Since viral diseases are spread during feeding, stopping whiteflies at early nymphal or adult stages is critical for preventing infection in tomato, cotton, and cucurbit crops. - Crop Protection During Critical Growth Stages
Vegetables and fruiting plants are highly sensitive during flowering and fruit set. Whitefly feeding at these stages causes yield and quality losses. Preventative insecticide programs ensure crop safety during these high-risk windows.
POMAIS Approach to Whitefly Control
At POMAIS, we advocate for an active ingredient rotation strategy using multiple modes of action to:
- Avoid resistance development
- Extend efficacy duration
- Maintain long-term population control
We offer both single-active and combination formulations for foliar and soil application, designed to match your crop, region, and pest pressure level. With full support in terms of label customization, documentation, and OEM production, you can confidently deliver results to your growers and clients.
In the next section, we’ll detail the specific POMAIS-recommended insecticide options—including systemic, contact, and dual-mode products—to help you choose the right tool for your market.
Recommended Insecticide Options from POMAIS
At POMAIS, we provide a full portfolio of insecticides tailored for whitefly control across vegetables, fruit trees, ornamentals, and greenhouse crops. Our formulations are available in various concentrations and packaging options, designed for both bulk buyers and branded distributors. Below are our key product categories organized by their action mode:
1. Contact-Kill Insecticides (Knockdown Adult Populations)
These formulations are designed to eliminate adult whiteflies quickly, reducing the chance of egg-laying and initial infestation spread.
Key Active Ingredients:
- Deltamethrin (EC/WP)
- Cypermethrin (EC/WP)
- Bifenthrin (SC)
Advantages:
- Fast knockdown effect within hours
- Suitable for rotation to reduce resistance buildup
- Effective for open-field crops and perimeter spraying
Recommended Use:
- Early outbreak suppression
- Combination with systemic agents for dual control
2. Systemic and Translaminar Insecticides (Target Immature Stages)
These products are absorbed into plant tissues and are highly effective against nymphs on the undersides of leaves, where contact sprays often fail.
Key Active Ingredients:
- Imidacloprid (SL/WG)
- Thiamethoxam (SC/WG)
- Acetamiprid (SP/SL)
- Dinotefuran (SL)
Advantages:
- Long residual activity (up to 2–3 weeks)
- Broad-spectrum control of sucking pests
- Ideal for foliar or soil application in vegetables and fruit crops
Recommended Use:
- High-pressure infestations
- Preventative programs in virus-prone crops
3. Combination Formulations (Dual-Mode Control & Resistance Management)
These products contain two active ingredients with complementary modes of action, enabling control of both adults and nymphs while minimizing resistance risks.
Key Combinations:
- Imidacloprid + Pyriproxyfen
→ Adult and juvenile hormone disruption - Thiamethoxam + Lambda-cyhalothrin
→ Systemic + contact knockdown synergy - Dinotefuran + Bifenthrin
→ Dual coverage for all life stages
Advantages:
- Controls multiple pest stages in a single spray
- Reduces application frequency
- Widely accepted in export markets
Recommended Use:
- High-value crops under whitefly and virus pressure
- Rotation programs in intensive cultivation systems

OEM & Service Support
All POMAIS insecticides are available with:
- Private label (OEM) branding
- Custom packaging volumes
- Multi-language GHS-compliant labeling
- MSDS, COA, and export documents
Whether you’re supplying greenhouse operations or managing broad-acre distribution, we ensure formulation consistency, shipment reliability, and regulatory compliance.
Application Strategy and Best Practices
To maximize the effectiveness of whitefly insecticides, you must go beyond product selection and apply them at the right time, with the correct technique and under the right conditions. Whether you are a grower, distributor, or spraying service provider, the following best practices will help you achieve optimal control using POMAIS products.
1. Timing: Spray Early and Repeat as Needed
- First application should target the early nymph stage, when populations are still low and before virus transmission or heavy feeding begins.
- For systemic products, apply preventively before peak infestation.
- For contact-kill products, apply at the onset of adult activity for quick knockdown.
- Under warm, humid conditions, plan for 7–14 day intervals depending on re-infestation pressure.
2. Spray Coverage and Technique
- Whiteflies concentrate on leaf undersides, so coverage must be complete.
- Use fine droplet nozzles and high-pressure sprayers for foliar applications.
- In crops with dense canopies (e.g., tomato, cotton), use angled nozzles or motorized atomizers to reach interior foliage.
- For greenhouse crops, ensure even horizontal spray movement to minimize canopy shadows.
3. Water Volume and Mixing
- Recommended spray volume: 300–500 L/ha for field crops, 500–1000 L/ha for orchards and greenhouse vegetables.
- Mix with clean, pH-neutral water for best chemical stability.
- Use non-ionic surfactants or oil-based adjuvants to improve leaf adherence and penetration, especially for waxy or hairy foliage.
4. Tank Mix and Resistance Management
- Rotate active ingredients from different IRAC groups to prevent resistance buildup.
- Avoid repeating the same insecticide group more than twice per crop cycle.
- For heavy infestations, mix contact + systemic products (if compatible) to target both adults and nymphs.
5. Environmental and Safety Considerations
- Avoid spraying under intense sunlight or high temperatures (>30°C) to reduce phytotoxicity risks.
- Apply in early morning or late afternoon for better absorption and operator safety.
- Wear full PPE during mixing and application; refer to product MSDS for handling instructions.
By following these practices, you can unlock the full performance potential of POMAIS insecticide formulations and ensure consistent, professional results in the field. Our technical team is available to advise on crop-specific application programs, tank-mix compatibility, and label adaptation for your market.
POMAIS: Your Supplier for Whitefly Insecticides
At POMAIS Agriculture, we understand that successful pest control is not just about product availability—it’s about providing reliable, market-ready solutions that perform consistently in the field. That’s why we deliver a full-spectrum portfolio of whitefly insecticides, backed by the service, documentation, and customization support needed to grow your business.
Why Distributors and Growers Choose POMAIS
- 10+ Years of Formulation and Export Experience
We serve importers, regional distributors, and large-scale agricultural projects across the Middle East, Africa, South America, Russia, and Central Asia. Our team has deep knowledge of local registration systems and product requirements. - Custom Manufacturing (OEM / ODM)
You can launch your own brand of whitefly insecticides with our private label service, offering:- Custom packaging: bottles, pouches, bulk drums
- Label design in multiple languages
- Variable concentrations to meet local use preferences
- Full Documentation Support
Every product is backed by:- MSDS and COA
- TDS (technical datasheet)
- Registration dossiers where needed
- Diverse Formulations to Match All Market Segments
Whether you supply open-field vegetable growers, orchard managers, greenhouse operations, or urban landscaping companies, we offer:- Contact-action EC and WP
- Systemic SC, SL, and WG
- Ready-to-sell combination formulations for resistance management
- Efficient Global Logistics
With a reliable manufacturing base and professional export handling, we ensure on-time delivery and stable inventory, even during seasonal demand peaks.
At POMAIS, we are committed to helping you supply products that work, sell, and scale. Whether you’re looking for a proven whitefly control solution or planning to build a private-label pesticide line, our team is ready to support your success.
Start Your Whitefly Control Program with POMAIS
If whiteflies are impacting your crop quality, spreading viral diseases, or increasing your pest management costs, now is the time to act with a proven, professional insecticide strategy.
At POMAIS Agriculture, we make it easy for you to:
- Get detailed product information on the most suitable formulations for your region, crops, and climate
- Request trial samples for evaluation and field performance testing
- Access technical documents (MSDS, COA, registration dossiers) for fast import and compliance
- Launch your own brand with OEM packaging, customized labeling, and multilingual support
- Build a long-term supply partnership backed by stable quality, timely delivery, and responsive service
We’re here to help you deliver results—whether you serve vegetable farms, orchards, greenhouses, or landscaping clients. Let’s build your next whitefly control program with confidence, speed, and consistency.
Contact our team today to get started.
Why Effective Whitefly Control Matters
If you’re managing large-scale vegetable fields, greenhouses, orchards, or ornamental nurseries, whiteflies are one of the most persistent and economically damaging pests you face. These tiny sap-sucking insects are not only capable of rapid population explosions in warm climates, but they also cause extensive plant damage, spread viruses, and contaminate leaves and fruit with honeydew and black sooty mold.
Once established, whitefly infestations are difficult to reverse without fast-acting and properly selected insecticides. Relying solely on environmental factors or natural predators may not deliver consistent or sufficient results—especially under commercial production timelines where yield loss translates directly into revenue loss.
At POMAIS, we support agricultural input distributors and growers with professional-grade insecticide solutions that are designed to:
- Deliver quick knockdown of whitefly adults and nymphs
- Penetrate leaf surfaces to control hidden or resistant stages
- Maintain control over multiple generations with long-lasting action
- Fit seamlessly into high-frequency production cycles with minimal phytotoxicity
This guide will help you understand:
- How to identify key whitefly species
- The damage they cause across crop types
- The most effective insecticide categories and active ingredients
- How POMAIS products can support your control program through custom formulations and flexible supply
If whiteflies are compromising your crop quality or creating product rejection risks, now is the time to implement a chemical control plan that works. Let’s begin with how to correctly identify the pest before treatment.
Key Identification Features of Whiteflies
Accurate identification is essential before selecting any control strategy. Whiteflies may be small, but their biological traits make them highly adaptable and destructive—especially in warm, irrigated environments where they breed rapidly and target a wide range of crops and ornamentals.
Whiteflies are not true flies (Diptera) but belong to the insect order Hemiptera, closely related to aphids and scales. They are characterized by their soft yellowish bodies and four powdery-white wings. While adults are easy to spot on the underside of leaves, the more damaging stage is often the nymph, particularly the later immature stages which feed heavily and remain immobile.

Key Life Stages to Watch
- Eggs: Tiny, oblong, usually deposited in circles or spirals on the underside of leaves.
- First Instar (Crawler): Only mobile immature stage; disperses briefly before settling.
- Later Nymphs (Instars 2–4): Immobile, flat, oval-shaped. Often mistaken for scale insects. This is the most critical stage to target with systemic insecticides.
- Adults: Winged, white, and visible when disturbed. Adults are the reproductive stage, and their elimination is essential to halt egg-laying.
Common Pest Species to Monitor
- Greenhouse Whitefly (Trialeurodes vaporariorum)
Found on vegetables, herbs, and ornamentals. Recognized by long waxy filaments around mature nymphs. - Sweetpotato Whitefly (Bemisia tabaci)
One of the most economically damaging species. Feeds on vegetables, cotton, and many ornamentals. Adults hold their wings at a slight angle and nymphs lack waxy fringes. - Giant Whitefly (Aleurodicus dugesii)
Easily identified by its long wax spirals and large white adults. Common in tropical ornamentals. - Citrus Whitefly, Mulberry Whitefly, and Woolly Whitefly
Found in orchards and landscaping systems. Their nymphs often have distinctive wax patterns, making visual diagnosis possible with basic magnification.
Understanding which species you’re facing—and the proportion of adults versus nymphs—allows you to select the appropriate formulation (contact vs. systemic) and application method (foliar vs. soil treatment). At POMAIS, we help our partners match insecticide recommendations not only by crop but by target species and development stage, ensuring higher control rates and fewer repeat applications.
Whitefly Damage in Field and Greenhouse Systems
Whiteflies are not merely a nuisance—they are a high-impact pest capable of causing significant crop damage, economic losses, and post-harvest quality degradation. If left unchecked, even moderate populations can escalate quickly in warm, humid environments, especially in protected structures like greenhouses or under intensive irrigation systems.
Direct Plant Damage
- Sap Extraction and Leaf Deformation
Nymphs and adults pierce the phloem to suck plant juices, leading to leaf yellowing, curling, desiccation, and premature drop. In crops like tomato, pepper, and cotton, this weakens the plant, reducing yield and fruit quality. - Stunted Growth and Plant Decline
Continuous feeding from multiple generations weakens young plants, delays maturity, and can cause widespread plant collapse in high-pressure situations. - Honeydew Production and Black Sooty Mold
As whiteflies feed, they excrete large volumes of sticky honeydew. This residue encourages the growth of black sooty mold, reducing photosynthetic capacity and contaminating produce. Leaf surfaces become unsightly, reducing the market value of leafy vegetables and ornamental crops.
Virus Transmission and Crop Loss
- Certain whitefly species, especially Bemisia tabaci (sweetpotato whitefly), act as vectors for serious plant viruses, including:
- Tomato yellow leaf curl virus (TYLCV)
- Cucurbit yellow stunting disorder virus
- Cotton leaf curl virus
- Viral diseases spread rapidly through fields and greenhouses, and insecticide-based whitefly control is the only reliable method of breaking the infection cycle.
Commercial and Post-Harvest Impact
- Residue concerns: Honeydew and sooty mold can lead to export rejection in high-value vegetable shipments.
- Visual degradation: Ornamental plant quality declines sharply under whitefly infestation.
- Increased labor: Growers must spend more on pruning, cleaning, and replacing damaged plants.
- Input inefficiencies: Whiteflies reduce the efficiency of irrigation, fertilization, and foliar nutrient uptake by damaging the foliage.
In high-density production systems, whiteflies cannot be managed effectively without targeted chemical control. Contact insecticides may eliminate adults quickly, but only systemic and translaminar products can penetrate the leaf surface and eliminate the feeding nymphs—the stage responsible for most economic damage.
POMAIS offers insecticide solutions specifically designed to:
- Interrupt virus transmission pathways
- Suppress both adult and nymphal stages
- Maintain leaf health and crop vigor under pest pressure
Chemical Control as the Primary Management Strategy
When facing aggressive whitefly infestations—particularly in high-value crops such as tomatoes, cucurbits, peppers, and ornamentals—chemical insecticides remain the most effective and scalable solution. In many commercial operations, environmental and biological controls are insufficient to halt pest outbreaks or prevent virus spread in time. This is where professional-grade insecticides from POMAIS deliver maximum impact.
Why Insecticides Are Essential
- Rapid Knockdown of Adults
Eliminating the reproductive population prevents egg-laying and suppresses immediate expansion. Contact insecticides are ideal for this stage, especially during initial outbreaks. - Systemic Penetration of Immature Stages
Whitefly nymphs (especially 2nd–4th instars) are immobile and located on leaf undersides—only systemic and translaminar insecticides can reach and eliminate them effectively. - Virus Transmission Suppression
Since viral diseases are spread during feeding, stopping whiteflies at early nymphal or adult stages is critical for preventing infection in tomato, cotton, and cucurbit crops. - Crop Protection During Critical Growth Stages
Vegetables and fruiting plants are highly sensitive during flowering and fruit set. Whitefly feeding at these stages causes yield and quality losses. Preventative insecticide programs ensure crop safety during these high-risk windows.
POMAIS Approach to Whitefly Control
At POMAIS, we advocate for an active ingredient rotation strategy using multiple modes of action to:
- Avoid resistance development
- Extend efficacy duration
- Maintain long-term population control
We offer both single-active and combination formulations for foliar and soil application, designed to match your crop, region, and pest pressure level. With full support in terms of label customization, documentation, and OEM production, you can confidently deliver results to your growers and clients.
In the next section, we’ll detail the specific POMAIS-recommended insecticide options—including systemic, contact, and dual-mode products—to help you choose the right tool for your market.
Recommended Insecticide Options from POMAIS
At POMAIS, we provide a full portfolio of insecticides tailored for whitefly control across vegetables, fruit trees, ornamentals, and greenhouse crops. Our formulations are available in various concentrations and packaging options, designed for both bulk buyers and branded distributors. Below are our key product categories organized by their action mode:
1. Contact-Kill Insecticides (Knockdown Adult Populations)
These formulations are designed to eliminate adult whiteflies quickly, reducing the chance of egg-laying and initial infestation spread.
Key Active Ingredients:
- Deltamethrin (EC/WP)
- Cypermethrin (EC/WP)
- Bifenthrin (SC)
Advantages:
- Fast knockdown effect within hours
- Suitable for rotation to reduce resistance buildup
- Effective for open-field crops and perimeter spraying
Recommended Use:
- Early outbreak suppression
- Combination with systemic agents for dual control
2. Systemic and Translaminar Insecticides (Target Immature Stages)
These products are absorbed into plant tissues and are highly effective against nymphs on the undersides of leaves, where contact sprays often fail.
Key Active Ingredients:
- Imidacloprid (SL/WG)
- Thiamethoxam (SC/WG)
- Acetamiprid (SP/SL)
- Dinotefuran (SL)
Advantages:
- Long residual activity (up to 2–3 weeks)
- Broad-spectrum control of sucking pests
- Ideal for foliar or soil application in vegetables and fruit crops
Recommended Use:
- High-pressure infestations
- Preventative programs in virus-prone crops
3. Combination Formulations (Dual-Mode Control & Resistance Management)
These products contain two active ingredients with complementary modes of action, enabling control of both adults and nymphs while minimizing resistance risks.
Key Combinations:
- Imidacloprid + Pyriproxyfen
→ Adult and juvenile hormone disruption - Thiamethoxam + Lambda-cyhalothrin
→ Systemic + contact knockdown synergy - Dinotefuran + Bifenthrin
→ Dual coverage for all life stages
Advantages:
- Controls multiple pest stages in a single spray
- Reduces application frequency
- Widely accepted in export markets
Recommended Use:
- High-value crops under whitefly and virus pressure
- Rotation programs in intensive cultivation systems

OEM & Service Support
All POMAIS insecticides are available with:
- Private label (OEM) branding
- Custom packaging volumes
- Multi-language GHS-compliant labeling
- MSDS, COA, and export documents
Whether you’re supplying greenhouse operations or managing broad-acre distribution, we ensure formulation consistency, shipment reliability, and regulatory compliance.
Application Strategy and Best Practices
To maximize the effectiveness of whitefly insecticides, you must go beyond product selection and apply them at the right time, with the correct technique and under the right conditions. Whether you are a grower, distributor, or spraying service provider, the following best practices will help you achieve optimal control using POMAIS products.
1. Timing: Spray Early and Repeat as Needed
- First application should target the early nymph stage, when populations are still low and before virus transmission or heavy feeding begins.
- For systemic products, apply preventively before peak infestation.
- For contact-kill products, apply at the onset of adult activity for quick knockdown.
- Under warm, humid conditions, plan for 7–14 day intervals depending on re-infestation pressure.
2. Spray Coverage and Technique
- Whiteflies concentrate on leaf undersides, so coverage must be complete.
- Use fine droplet nozzles and high-pressure sprayers for foliar applications.
- In crops with dense canopies (e.g., tomato, cotton), use angled nozzles or motorized atomizers to reach interior foliage.
- For greenhouse crops, ensure even horizontal spray movement to minimize canopy shadows.
3. Water Volume and Mixing
- Recommended spray volume: 300–500 L/ha for field crops, 500–1000 L/ha for orchards and greenhouse vegetables.
- Mix with clean, pH-neutral water for best chemical stability.
- Use non-ionic surfactants or oil-based adjuvants to improve leaf adherence and penetration, especially for waxy or hairy foliage.
4. Tank Mix and Resistance Management
- Rotate active ingredients from different IRAC groups to prevent resistance buildup.
- Avoid repeating the same insecticide group more than twice per crop cycle.
- For heavy infestations, mix contact + systemic products (if compatible) to target both adults and nymphs.
5. Environmental and Safety Considerations
- Avoid spraying under intense sunlight or high temperatures (>30°C) to reduce phytotoxicity risks.
- Apply in early morning or late afternoon for better absorption and operator safety.
- Wear full PPE during mixing and application; refer to product MSDS for handling instructions.
By following these practices, you can unlock the full performance potential of POMAIS insecticide formulations and ensure consistent, professional results in the field. Our technical team is available to advise on crop-specific application programs, tank-mix compatibility, and label adaptation for your market.
POMAIS: Your Supplier for Whitefly Insecticides
At POMAIS Agriculture, we understand that successful pest control is not just about product availability—it’s about providing reliable, market-ready solutions that perform consistently in the field. That’s why we deliver a full-spectrum portfolio of whitefly insecticides, backed by the service, documentation, and customization support needed to grow your business.
Why Distributors and Growers Choose POMAIS
- 10+ Years of Formulation and Export Experience
We serve importers, regional distributors, and large-scale agricultural projects across the Middle East, Africa, South America, Russia, and Central Asia. Our team has deep knowledge of local registration systems and product requirements. - Custom Manufacturing (OEM / ODM)
You can launch your own brand of whitefly insecticides with our private label service, offering:- Custom packaging: bottles, pouches, bulk drums
- Label design in multiple languages
- Variable concentrations to meet local use preferences
- Full Documentation Support
Every product is backed by:- MSDS and COA
- TDS (technical datasheet)
- Registration dossiers where needed
- Diverse Formulations to Match All Market Segments
Whether you supply open-field vegetable growers, orchard managers, greenhouse operations, or urban landscaping companies, we offer:- Contact-action EC and WP
- Systemic SC, SL, and WG
- Ready-to-sell combination formulations for resistance management
- Efficient Global Logistics
With a reliable manufacturing base and professional export handling, we ensure on-time delivery and stable inventory, even during seasonal demand peaks.
At POMAIS, we are committed to helping you supply products that work, sell, and scale. Whether you’re looking for a proven whitefly control solution or planning to build a private-label pesticide line, our team is ready to support your success.
Start Your Whitefly Control Program with POMAIS
If whiteflies are impacting your crop quality, spreading viral diseases, or increasing your pest management costs, now is the time to act with a proven, professional insecticide strategy.
At POMAIS Agriculture, we make it easy for you to:
- Get detailed product information on the most suitable formulations for your region, crops, and climate
- Request trial samples for evaluation and field performance testing
- Access technical documents (MSDS, COA, registration dossiers) for fast import and compliance
- Launch your own brand with OEM packaging, customized labeling, and multilingual support
- Build a long-term supply partnership backed by stable quality, timely delivery, and responsive service
We’re here to help you deliver results—whether you serve vegetable farms, orchards, greenhouses, or landscaping clients. Let’s build your next whitefly control program with confidence, speed, and consistency.
Contact our team today to get started.